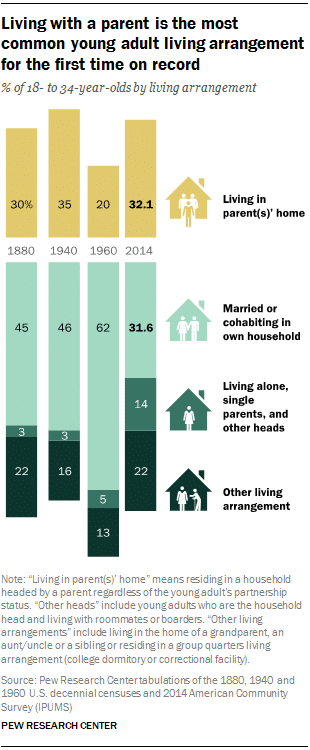Curiosity about the age of first-time parents is natural as we ponder the changing landscapes of family dynamics and societal trends. In this article, we embark on a journey to uncover the average age at which individuals embark on their parenting journey for the first time. Through examining noteworthy statistics and revealing insights, we aim to shed light on the age range that typically defines this significant milestone in one’s life. Prepare to be captivated by the fascinating data that awaits us.
Review contents
Factors Affecting Age for First-time Parents
Biological Factors
Biological factors play a significant role in determining the age at which individuals become first-time parents. Women’s fertility gradually declines after their 20s, with a more pronounced decline after the age of 35. As a result, many women feel a sense of urgency to start a family before their fertility decreases further. On the other hand, men generally have a more extended period of fertility, although their sperm quality may decline with age.
Socioeconomic Factors
Socioeconomic factors also influence the age at which individuals become first-time parents. Factors such as income level, employment stability, and access to healthcare can all impact the decision to start a family. Couples with lower incomes may delay parenthood due to financial constraints, while those with stable jobs and higher incomes may feel more secure in their ability to provide for a child.
Cultural Factors
Cultural norms and values can greatly influence the age at which individuals choose to become parents. In some cultures, there may be societal pressure to have children at a younger age, while in others, the focus may be on career and personal fulfillment before starting a family. Cultural expectations of gender roles and family dynamics can also shape individuals’ decisions regarding parenthood.
Education Level
Education level is another factor that can impact the age at which individuals become first-time parents. Pursuing higher education, such as completing a college degree or advanced degrees, often requires a significant time commitment. Many individuals choose to delay parenthood until after they have achieved their educational goals and established a stable career.
Career Priorities
Career priorities can also play a significant role in determining the age at which individuals become first-time parents. Those who are ambitious and dedicated to their professional aspirations may choose to delay parenthood to focus on advancing in their careers. The demands of certain professions, such as long working hours or frequent travel, may also make it challenging to balance work and family life.
Relationship Stability
The stability of one’s relationship is an essential factor in the decision to become a first-time parent. Couples who have been together for a longer time and have established a strong foundation may feel more confident in their ability to navigate the challenges of parenthood. Conversely, those in less stable or new relationships may choose to delay starting a family until their relationship is more secure.
Trends in Age for First-time Parents
Average Age for First-time Parents
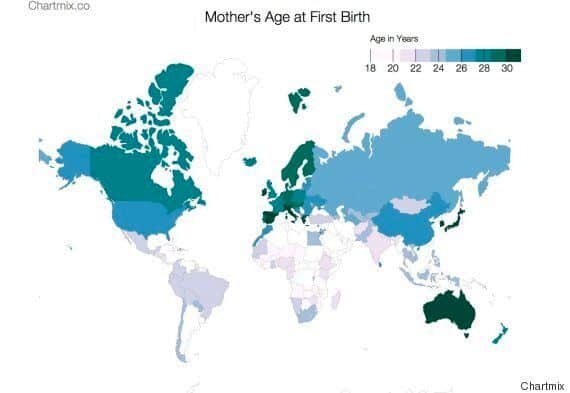
The average age at which individuals become first-time parents has been steadily increasing over the past few decades. In many developed countries, the average age for women to have their first child is now in the late 20s or early 30s. This upward trend can be attributed to various factors, including greater access to education, career opportunities, and advancements in reproductive technologies.
Gender Differences
There are also gender differences when it comes to the age at which individuals become first-time parents. On average, men tend to become fathers slightly later than women. This can be attributed to factors such as biological differences in fertility, career considerations, and societal expectations regarding gender roles.
Regional Differences
Age at first-time parenthood can vary significantly between regions and countries. Factors such as cultural norms, economic conditions, and access to healthcare can all contribute to regional differences. For example, in some countries with strong social support systems, individuals may feel more comfortable starting a family at a younger age, knowing that they will have access to resources and assistance.
Variations over Time
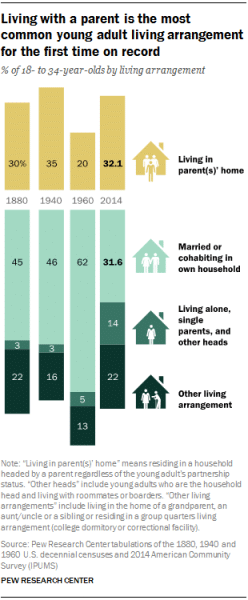
Over time, societal attitudes and norms surrounding parenthood have evolved, leading to variations in the age at which individuals become first-time parents. In the past, it was more common for individuals to start a family at a younger age, often right after marriage. However, as societal values and expectations have shifted, individuals now have more freedom and choice in deciding when to become parents.
This image is property of d25d2506sfb94s.cloudfront.net.
Advantages and Challenges of Being Young Parents
Increased Energy and Resilience
One advantage of being a young parent is the increased energy and resilience that often comes with youth. Younger parents may find it easier to keep up with the physical demands of caring for a child, such as sleepless nights and constant supervision. They may also have more natural stamina to participate in activities and play with their children.
Ability to Relate to Children
Being closer in age to their children can allow young parents to relate more easily to their child’s experiences and interests. They may have a better understanding of the challenges and pressures that children face in school and social settings. This can facilitate a closer parent-child relationship and foster effective communication.
Financial Challenges
However, being a young parent can also bring forth financial challenges. Younger parents may still be establishing their careers and may have limited financial resources. This can make it harder to provide for their child’s needs and can place stress on the family.
Limited Life Experiences
Young parents may also have limited life experiences compared to older parents. They may not have had as much time to travel, pursue personal goals, or explore their own interests before becoming parents. This can lead to feelings of missing out or a sense of needing to put aside personal aspirations to prioritize their child’s upbringing.
Advantages and Challenges of Being Older Parents
Emotional and Financial Stability
One advantage of being older parents is that they often have greater emotional and financial stability. They may have had more time to establish a stable career and accumulate financial resources, providing a secure foundation for their child’s future. Older parents may also have more life experience and emotional maturity, allowing them to handle the challenges of parenthood with a greater sense of confidence.
Established Relationships
Older parents may also have more established and mature relationships. They may have been together for a longer time, allowing them to develop a strong foundation of trust and communication. This can foster a stable and supportive environment for raising children.
Greater Life Experiences
Older parents often have a wealth of life experiences and wisdom to draw upon when raising their children. They may have acquired valuable skills and knowledge throughout their lives, which can benefit their parenting approach. The breadth of their experiences can also enrich the child’s upbringing, exposing them to a wider range of perspectives and opportunities.
Declining Fertility
One challenge that older parents may face is declining fertility. As individuals age, their fertility decreases, and the chances of conceiving naturally decline. This can lead to greater difficulties in achieving pregnancy and may require the use of assisted reproductive technologies.
Increased Health Risks
Older parents may also face increased health risks during pregnancy and childbirth. Advanced maternal age is associated with a higher risk of conditions such as gestational diabetes, high blood pressure, and complications during delivery. For older fathers, there is some evidence suggesting an increased risk of certain genetic conditions in their offspring.
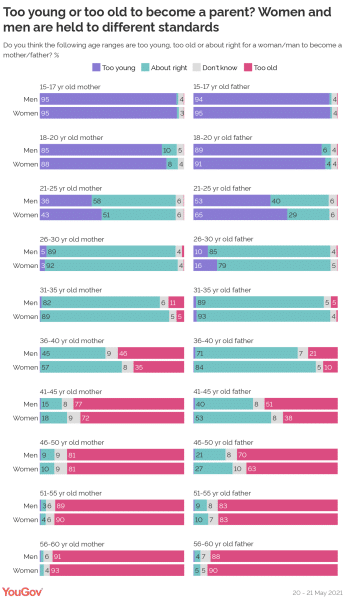
This image is property of www.bgsu.edu.
Factors Influencing the Decision to Delay Parenthood
Pursuing Higher Education
One common factor influencing the decision to delay parenthood is the pursuit of higher education. Many individuals prioritize their educational goals and choose to delay starting a family until they have completed their studies or achieved a certain level of education.
Career Advancement
Career advancement is another significant factor that may lead individuals to delay parenthood. Focusing on career development and establishing oneself professionally can require time and energy, making it challenging to balance the demands of work and parenthood. Some individuals may choose to prioritize their careers first and delay starting a family until they feel more established in their professional lives.
Financial Stability
The desire to achieve financial stability before starting a family is another factor that may lead to the decision to delay parenthood. Raising a child can be expensive, and many individuals want to ensure that they have the financial resources to provide for their child’s needs. This often involves saving money, paying off debts, and establishing a secure financial foundation.
Relationship Readiness
The readiness of the relationship is a crucial factor in deciding when to become parents. Couples may choose to delay starting a family until they feel their relationship is stable and strong enough to support the challenges of parenthood. Taking the time to cultivate a healthy and supportive partnership can contribute to a more positive parenting experience.
Impacts of Delaying Parenthood
Increased Risk of Infertility
Delaying parenthood can increase the risk of infertility, especially for women. As women age, the quantity and quality of their eggs decrease, making it more challenging to conceive naturally. This can lead to a longer and more difficult journey to parenthood, sometimes requiring medical interventions.
Difficulty Conceiving Naturally
Delayed parenthood can also result in increased difficulty conceiving naturally. The chances of getting pregnant naturally decrease with age, and individuals may experience longer periods of trying to conceive or require more invasive fertility treatments.
Use of Assisted Reproductive Technologies
Many individuals who delay parenthood may turn to assisted reproductive technologies, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), to help them conceive. These treatments can be physically, emotionally, and financially demanding, adding an additional layer of complexity to the process of becoming parents.
Maternal and Paternal Health Risks
There are also potential health risks associated with delayed parenthood. Advanced maternal age during pregnancy is linked to an increased risk of conditions such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and chromosomal abnormalities. Additionally, older fathers may have a higher likelihood of passing on genetic mutations to their offspring.
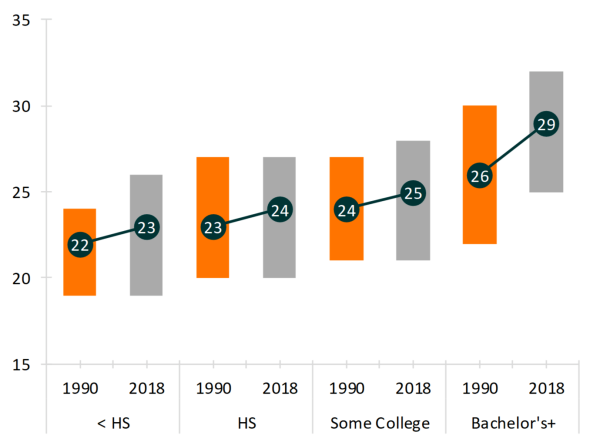
This image is property of static01.nyt.com.
Social and Cultural Attitudes Toward Older Parents
Ageism and Stereotypes
Social and cultural attitudes toward older parents can be influenced by ageism and stereotypes. Some individuals may hold the misconception that older parents are less capable or less energetic when it comes to parenting. Ageist beliefs can marginalize and undermine the experiences and abilities of older parents.
Perceived Parenting Competence
There may also be societal perceptions regarding the competence of older parents. Some may assume that younger parents have an advantage in relating to and understanding their children’s needs. Older parents may need to navigate challenges such as proving their parenting abilities and addressing assumptions about their ability to keep up with younger children.
Potential Judgment and Criticism
Older parents may face judgment or criticism from others. Friends, family members, and even strangers may question their decision to start a family later in life, leading to feelings of insecurity or the need to justify their choices. It is essential to recognize that age alone does not determine one’s ability to be a loving and capable parent.
Psychological and Emotional Factors for First-time Parents
Maturity and Emotional Preparedness
Psychological and emotional factors play a crucial role for first-time parents, regardless of age. Maturity and emotional preparedness can contribute to a smoother adjustment to parenthood and parental role responsibilities. Understanding one’s own emotions, strengths, and limitations can help parents navigate the challenges of parenting with greater confidence.
Adjustment to Parenthood
Adjusting to parenthood can be a challenging process, especially for first-time parents. The experience of becoming a parent brings significant lifestyle changes, increased responsibilities, and sleep deprivation. Younger parents may find it harder to adapt to these changes due to their limited life experiences, while older parents may have a better understanding of the adjustments needed and cope more effectively.
Bonding with the Child
Creating a strong bond with one’s child is a central goal for many first-time parents. The ability to form a secure attachment with a child can be influenced by various factors, including a parent’s emotional availability, responsiveness, and understanding of child development. Both younger and older parents can develop a deep and loving bond with their child through consistent care, nurturing, and affection.
This image is property of img.huffingtonpost.com.
Support and Resources for First-time Parents
Informative Programs and Classes
Informative programs and classes can be valuable resources for first-time parents. These educational opportunities provide information on various aspects of parenting, such as child development, breastfeeding, and nutrition. They also offer a platform for parents to connect with others who are going through similar experiences, fostering a sense of community and support.
Parenting Communities and Support Networks
Joining parenting communities and support networks can offer a sense of belonging and a space for sharing experiences and advice. These groups can provide emotional support, practical tips, and a network of individuals who understand the joys and challenges of parenthood.
Mental Health Services
Mental health services are essential for supporting the well-being of first-time parents. Parenthood can bring forth a range of emotions, from joy and fulfillment to stress and anxiety. Access to mental health professionals, such as therapists or counselors, can provide guidance and support to navigate the emotional challenges that may arise.
Financial Assistance
Financial assistance programs can help alleviate some of the financial burdens associated with parenthood. These programs can provide support in the form of childcare subsidies, healthcare coverage, and access to affordable housing. Having access to such assistance can help reduce stress and enable parents to provide for their child’s needs more effectively.
Conclusion
The decision of when to become a first-time parent is multifaceted, influenced by a variety of factors including biological, socioeconomic, cultural, and personal considerations. Age at first-time parenthood has been shifting in recent years, with individuals choosing to delay starting a family for various reasons. While there are advantages and challenges associated with both young and older parenthood, each stage of life brings unique experiences and perspectives to the parenting journey. It is important to recognize that there is no one-size-fits-all approach and that the decision to become a parent is deeply personal. Support and resources are available to help individuals navigate the challenges and joys of parenthood, regardless of their age.
This image is property of www.pewresearch.org.